What Are Managed IT Services? Meaning, Types, Benefits and Challenges
Managed IT services allow businesses to outsource IT infrastructure tasks to a third-party vendor, known as a managed services provider (MSP).
-
-
- Managed IT services are outsourced information technology functions and tasks (i.e., implementing and maintaining infrastructure on an ongoing basis) where a third-party vendor handles the work.
- The task or function outsourced in a managed IT services arrangement comprises the managed IT service, and the third-party vendor is the managed services provider (MSP).
- This article weighs the benefits and challenges of managed IT services and describes many of the different types of services available.
Table of Contents
What Are Managed IT Services?
Managed IT services allow businesses to outsource information technology functions (e.g., backup, security, help desk) to a third-party vendor. The solution rendered comprises the managed IT service and the vendor performing the work is the managed services provider (MSP).
-
- There are many types of managed IT services, but the concept behind them all is to shift the internal responsibility of ongoing IT maintenance to a service provider. MSPs are often local organizations that can service a client on-site, but they might also operate remotely or even from an offshore location.
-
Various Elements of Managed IT Services
Source: Hitachi
How do Managed IT Services Work?
- In a managed IT services agreement, an MSP is responsible for continuing operation of technology solutions or infrastructure. In return, the client pays a recurring fee, typically monthly (but sometimes quarterly or yearly). Effective managed services relationships can free up internal resources that might have gone to managing IT tasks and provide businesses with predictable pricing, which can help in the IT budgeting process.
- The terms of a managed IT services arrangement are outlined in service level agreements (SLAs), which help set expectations between client and vendor. The SLA contract holds the MSP accountable for specified services and defines by which metrics quality of service delivery will be evaluated. SLAs typically have provisions for outages, recovery procedures, and technical assistance.
Why do businesses use managed IT services?
-
- From enhancing operations to simplifying IT administration to bringing in outside expertise, there are many reason to us managed IT services. According to data from the 2025 State of IT, companies of all sizes use managed IT services, and nearly three-fourths of organizations use at least one MSP.
-
- The need for managed IT services is influenced by a wide range of variables, including:
-
-
- Pressure on organizations to take advantage of current technological trends.
- Lack of time or technical skills within an organization
- Desire to mitigate the risk of growing cybersecurity threats
- The need to ensure regulatory compliance
- The potential to save money by outsourcing specific IT tasks
- Pressure on organizations to take advantage of current technological trends.
-
-
- The need for managed IT services is influenced by a wide range of variables, including:
-
How are managed IT services priced?
A managed services provider may charge fees according to several models. Examples of cost structures include per-device, per-user, all-inclusive pricing, or tiered pricing.
- Per-device pricing model: Calculated based on a fixed cost for every device (e.g., servers, laptops, or desktops) managed. For example, an MSP offering a remote management and monitoring service might charge a monthly fee of $300 per server and $50 per client device.
- Per-user pricing model: Flat fee calculated by the number of users an MSP supports. If a business’s employees each use several devices (e.g., a notebook, iPad, and smartphone), it might be more cost-effective to seek out an MSP that offers a per-user model.
- All-inclusive pricing: A fixed flat fee for an agreed-upon range of services offered by an MSP for a contracted time period. This model can provide predictability for the client while reducing complexity.
- Tiered pricing: A model that offers multiple package deals, often with good, better, and best options where costs rise with the quality or quantity of bundled services.
- Typically, managed IT services are priced on a recurring basis, with monthly costs being common—MSPs often prefer the predictability of a recurring monthly revenue stream. See More: What Is AWS? Overview, Services, and Pricing Calculator
-
How much do businesses spend on managed IT services?
- According to the 2025 State of IT report, an annual survey of IT professionals, managed services account for 10% of overall IT spending (which also includes budget for hardware, software, cloud, IT labor, facilities and power, telecom, and internal services).
- In other words, if an organization has a $1M annual IT budget, $100K goes towards managed services, on average. Looking at the cost of individual managed IT services, organizations spend the most on managed security and the least on managed print services.
-
10 Types of Managed IT Services
- Below are 10 common types of managed IT services:
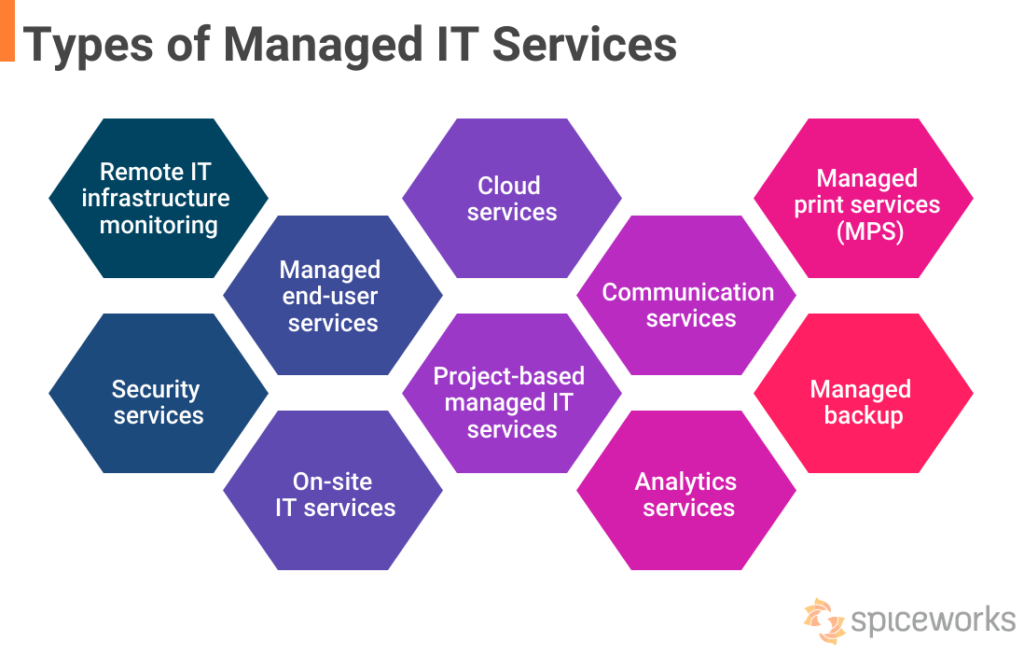
Managed IT Services Types
1. Remote IT infrastructure monitoring
Remote management and monitoring of servers, workstations, and mobile devices is an often essential core service offered by MSPs. From an MSP business perspective, competition in this space can be intense, which could allow clients to strike a favorable deal if they shop around.
2. Security services
Businesses are tasked with securing their environments from an ever-growing number of cyber threats, but many organizations lack the in-house resources to do so. As organizations worry about device and data security, MSPs have established their managed security services or resell cybersecurity solutions through partnerships with security vendors.
3. Managed end-user services
End-user services may include a vast range of solutions, but they often center around assistance provided to an organization’s workers and customers. At the most fundamental level, end-user services include an outsourced IT help desk or service desk solution that helps answer questions or resolves technical issues with operating systems, devices, applications, connectivity, and more.
4. On-site IT services
Often known as managed field services, on-site IT services involve an MSP deploying technicians to a physical location to carry out a range of IT activities. This may include equipment installation or maintenance, break-fix repairs, cabling or wireless installations, site assessments, and more.
5. Cloud services
With the introduction of cloud technology, managed IT services have expanded to include cloud services. MSPs might manage an organization’s public cloud instances (e.g., IaaS or PaaS) with providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google, or Microsoft. Managed cloud services might also encompass the implementation phase of a cloud deployment (e.g., consulting, assessment, migration, etc).
See More: Cloud Controlled Wireless and Cloud Managed Wi-Fi: What’s the Difference?
6. Project-based managed IT services
When companies need help with important IT projects, they can benefit from collaborating with a managed service provider with experience and technical know-how. Examples of project-specific technology services might include help with the evaluation, implementation, and ongoing technical assistance with business solutions such as SharePoint or Salesforce. A competent MSP might also help keep a project on a given schedule and within a pre-defined budget.
7. Communication services
Enterprise communication tools often fall under the purview of IT departments, and managed communications services can help businesses manage systems for telephony, messaging, data, and video conferencing. Maintaining uptime, encrypting messages, securing video calls, and managing Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) licenses are key tasks that MSPs might provide.
8. Analytics services
MSPs offering managed data analytics services assist in gathering, assessing, and analyzing user and customer data. For example, a provider might monitor site traffic, social networking participation, and customer behavior, then analyze the data to surface insights that can help enhance business outcomes.
9. Managed print services (MPS)
Managed print services outsource printing demands to a third-party vendor, who might evaluate needs, replace hardware, perform maintenance, and restock printing supplies. Print services might also entail monitoring and reviewing printing activities to identify efficiencies and potentially to reduce overall expenditures.
10. Managed backup and recovery
Limited data backup may be bundled with many types of managed services (e.g., security and cloud services), but some providers offer additional, comprehensive backup and recovery solutions as a standalone option. Managed backup services may include identifying requirements, developing disaster recovery plans, regularly backing up data locally and to cloud providers, or retrieving and restoring data.
See More: Why Managed Wi-Fi Services Meet the Needs of Small and Medium-Sized Organizations
Benefits of Managed IT Services
Compared to managing IT processes in-house, using managed IT services can offer a wide variety of benefits, including:
1. Filling IT skills gaps
Managed services might help teams gain access to needed expertise (i.e., cybersecurity skills). Many service providers employ specialized talent that internal IT teams lack, and employing an MSP often makes more sense than trying to hire or develop in-house expertise. Additionally, using an MSP can free up IT professionals to concentrate on important initiatives instead of spreading time thinly across many projects.
2. Clearly-defined service availability
Because managed service providers maintain service availability in accordance with an SLA, businesses know what to anticipate. MSPs often monitor systems around the clock and can take remedial action more quickly than internal teams. With the backing of a reliable MSP, businesses can gain peace of mind when a trusted party is maintaining service levels and fixing technical issues in the event of an outage.
3. Improving internal IT productivity
Outsourcing select IT responsibilities to MSPs can help internal IT focus on more productive initiatives (i.e., less firefighting and more process improvements). Also, because managed IT service providers support many organizations, they often have extensive experience and exposure to best practices that can improve organizational efficiency.
4. Predictable expenditures and reduced upfront costs
Because MSP plans are paid for via a subscription, businesses often favor the predictability of this model, which can help organizations avoid large capital expenditures required when deploying and maintaining in-house infrastructure. Additionally, using managed IT services might also give businesses access to the latest technologies without the hassle and expense of upgrading them internally.
5. Reducing dependence on tribal knowledge
Within an organization, information and internal processes that are not documented are known as tribal knowledge. When employees leave an organization, they take their tribal knowledge with them, potentially resulting in a knowledge gap. When an organization uses an MSP that remains constant even amid internal turnover, processes can remain constant even when key hires leave.
See More: Why Managed Kubernetes as a Service Should Be a Part of Your DevOps Strategy
Challenges of Managed IT Services
Now that we have discussed the benefits associated with managed IT services let’s consider some of their challenges. When considering an MSP, keep the following in mind before you make the jump:
1. Service levels dependent on quality of MSP
As with any relationship, choosing the right partner is the key to success, and there are consequences for choosing poorly. Outsourcing IT duties to an unreliable vendor can result in dissatisfaction, poor levels of service, and even financial losses. When selecting an MSP, organizations should ensure SLAs are well-defined and that the MSP has the resources to adhere to the terms outlined within. Before entering an agreement with an MSP, make sure to properly vet the organization and perform due diligence before granting them access to your environment. Shopping around for MSPs is also a good idea, to ensure you find the right fit.
2. Outsourcing can cause its own headaches
No organization is perfect, including managed services providers. Because MSPs typically work with many customers, they might not necessarily be able to dedicate as much time or offer a personal touch as an in-house IT professional would. Even if technically knowledgeable, technicians working for a third-party vendor won’t know a business’s employees, understand its culture or have long-standing relationships within the organization. For example, a managed help desk might feel impersonal compared to one run internally, which could lead to lower satisfaction. Additionally, MSPs face the same challenges all organizations do, including difficulty finding and retaining talent, high employee turnover (burnout among IT professionals working in MSPs is common), and mistakes caused by human error.
-
3. An MSP can’t fix all of your problems
Outsourcing IT tasks to a third-party vendor is not a cure-all solution, it’s more akin to a relationship that has to be proactively managed if you want to get the most out of it. If you don’t check in with your MSP regularly, you might not get the attention you deserve or all of the services you have contracted them for. Many IT professionals stress the need to regularly review the SLA contract and request regular reporting on the work done. Although it does require some work, it’s also important to maintain open lines of communication so MSPs are familiar with your organization and your environment. When that communication breaks down, it can lead to misunderstandings, finger-pointing, and degraded levels of service.
4. Cybersecurity risks
Many organizations hire MSPs because they want to gain access to security expertise that they don’t have in-house. Ironically, because they manage a large number of clients, MSPs have become prime targets for cybercriminals. By compromising a single MSP, hackers might gain access to thousands of businesses and their devices, a big payoff for the attackers. As a result, an organization is only as secure as the suppliers it uses, and any breach along the supply chain can result in serious consequences. As part of your MSP vetting process, you should pay attention to an MSP’s record on security, compliance, and the preservation and protection of sensitive data. After all, you’re often giving MSPs the “keys to your castle,” so you need to be able to trust them.
5. Potential for cost overruns or sticker shock
One primary motivation for contracting a managed IT services provider is to reduce cost or bring predictability to IT expenditures. However, using an MSP is not always the cheapest option. Costs can sometimes be higher than expectations, especially at contract renewal time (especially if you were given a low introductory rate) or when you receive a quote for increasing the scope of your contract. There is also a degree of vendor lock-in when you outsource processes to an MSP, which could make it somewhat difficult to fire a services provider if you want to switch providers or bring tasks in-house. If costs do rise, there is the potential to remove some unused services from the contract to bring the price down.
See More: How to Optimize Your IT Infrastructure to Meet Edge Computing Requirements
Takeaway
Managed IT services won’t magically fix all of your tech problems, but when used effectively, they can help organizations (big and small) simplify processes, free up valuable time, bring in needed expertise, and provide IT budget predictability. However, as in relationships, IT departments should be intentional when choosing a partner—not settling for a sub-par MSP, clearly setting expectations at the start, and checking-in regularly to make sure they’re getting what they deserve.
Did this article help you understand the concept of managed services? Tell us on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
MORE ON CLOUD






